Redux源码解读 - combineReducers篇。
这次讲讲combineReducers这个函数。
其实之前学习过React,也用过和React配套的React-Redux。
combineReducers既然不知道它是干嘛的。
直接上官网找找文档就行了。
以下是在中文网摘过来的一段话。
随着应用变得越来越复杂,可以考虑将 reducer 函数 拆分成多个单独的函数,拆分后的每个函数负责独立管理state的一部分。combineReducers辅助函数的作用是,把一个由多个不同reducer函数作为value的object,合并成一个最终的 reducer函数,然后就可以对这个reducer调用createStore方法。合并后的reducer可以调用各个子reducer,并把它们返回的结果合并成一个state对象。combineReducers()返回的state对象,会将传入的每个reducer返回的state按其传递给combineReducers()时对应的key进行命名。
不是很难理解。
如果把全部的处理action的逻辑写在一个reducer,这个reducer就会显得很臃肿,也不容易维护。
合并不同处理逻辑的reducer,返回一个新的reducer,通过新的reducer来创建store。
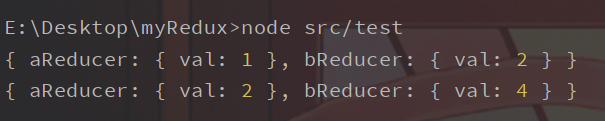
可以写个小例子来看看这个函数的效果:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 const aReducer = (state = { val: 1 }, action ) => { switch (action.type ) { case "increment" : return { ...state, val : state.val + 1 , }; case "decrement" : return { ...state, val : state.val - 1 , }; default : return state; } }; const bReducer = (state = { val: 2 }, action ) => { switch (action.type ) { case "increment" : return { ...state, val : state.val + 2 , }; case "decrement" : return { ...state, val : state.val - 2 , }; default : return state; } }; const reducer = combineReducers ({ aReducer, bReducer, }); const store = createStore (reducer);console .log (store.getState ());store.subscribe (() => { console .log (store.getState ()); }); store.dispatch ({ type : "increment" , });
运行之后可以出现:
到这里基本就可以明白基本的流程了。
每个reducer都有自己的一个命名,这个命名会在state中体现。
每次dispatch,会遍历每一个传入的reducer,更新state。
ok,那先把源码贴上来:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 export default function combineReducers (reducers ) { const reducerKeys = Object .keys (reducers); const finalReducers = {}; for (let i = 0 ; i < reducerKeys.length ; i++) { const key = reducerKeys[i]; if (process.env .NODE_ENV !== "production" ) { if (typeof reducers[key] === "undefined" ) { warning (`No reducer provided for key "${key} "` ); } } if (typeof reducers[key] === "function" ) { finalReducers[key] = reducers[key]; } } const finalReducerKeys = Object .keys (finalReducers); let unexpectedKeyCache; if (process.env .NODE_ENV !== "production" ) { unexpectedKeyCache = {}; } let shapeAssertionError; try { assertReducerShape (finalReducers); } catch (e) { shapeAssertionError = e; } return function combination (state = {}, action ) { if (shapeAssertionError) { throw shapeAssertionError; } if (process.env .NODE_ENV !== "production" ) { const warningMessage = getUnexpectedStateShapeWarningMessage ( state, finalReducers, action, unexpectedKeyCache ); if (warningMessage) { warning (warningMessage); } } let hasChanged = false ; const nextState = {}; for (let i = 0 ; i < finalReducerKeys.length ; i++) { const key = finalReducerKeys[i]; const reducer = finalReducers[key]; const previousStateForKey = state[key]; const nextStateForKey = reducer (previousStateForKey, action); if (typeof nextStateForKey === "undefined" ) { const errorMessage = getUndefinedStateErrorMessage (key, action); throw new Error (errorMessage); } nextState[key] = nextStateForKey; hasChanged = hasChanged || nextStateForKey !== previousStateForKey; } hasChanged = hasChanged || finalReducerKeys.length !== Object .keys (state).length ; return hasChanged ? nextState : state; }; }
看起来很长,拆开开其实就会很清晰。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 const reducerKeys = Object .keys (reducers);const finalReducers = {};for (let i = 0 ; i < reducerKeys.length ; i++) { const key = reducerKeys[i]; if (process.env .NODE_ENV !== "production" ) { if (typeof reducers[key] === "undefined" ) { warning (`No reducer provided for key "${key} "` ); } } if (typeof reducers[key] === "function" ) { finalReducers[key] = reducers[key]; } } const finalReducerKeys = Object .keys (finalReducers);
第一段代码。
先是获取了每个reducer的名字,存到reducerKeys里面。
定义了一个字面对象量finalReducers。
然后根据reducerKeys的长度做了一个循环。
这个循环两个判断。
第一个判断,如果传入了一个值为undefined的属性,非生产环境下就会有一个警告。
第二个判断,只把值的类型为function的才添加到finalReducers里面。
循环结束后获取finalReducers的属性名组成的数组,存到finalReducerKeys。
这段的作用就是防止传入不符合规则的对象。
比如下面这样:
1 2 3 4 5 combineReducers ({ a : undefined , b : 1 , c : "abc" , });
这些属性名对应的值都是不符合规则的,都要排除掉。
1 2 3 4 let unexpectedKeyCache;if (process.env .NODE_ENV !== "production" ) { unexpectedKeyCache = {}; }
第二段代码。
就在非生产环境下初始化一个字面对象变量unexpectedKeyCache而已,现在还不知是干什么的,先跳过。
1 2 3 4 5 6 let shapeAssertionError;try { assertReducerShape (finalReducers); } catch (e) { shapeAssertionError = e; }
第三段代码
往函数assertReducerShape传入了finalReducers变量。
对函数assertReducerShape的运行进行了异常捕获。
来看看assertReducerShape这个函数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 function assertReducerShape (reducers ) { Object .keys (reducers).forEach ((key ) => { const reducer = reducers[key]; const initialState = reducer (undefined , { type : ActionTypes .INIT }); if (typeof initialState === "undefined" ) { throw new Error ( `Reducer "${key} " returned undefined during initialization. ` + `If the state passed to the reducer is undefined, you must ` + `explicitly return the initial state. The initial state may ` + `not be undefined. If you don't want to set a value for this reducer, ` + `you can use null instead of undefined.` ); } if ( typeof reducer (undefined , { type : ActionTypes .PROBE_UNKNOWN_ACTION (), }) === "undefined" ) { throw new Error ( `Reducer "${key} " returned undefined when probed with a random type. ` + `Don't try to handle ${ActionTypes.INIT} or other actions in "redux/*" ` + `namespace. They are considered private. Instead, you must return the ` + `current state for any unknown actions, unless it is undefined, ` + `in which case you must return the initial state, regardless of the ` + `action type. The initial state may not be undefined, but can be null.` ); } }); }
这里面主要对每个reducer做了两个判断。
第一个判断,初始化时对于传进的初始状态undefined不能返回undefined。
必须在Redux内部初始化时(调用一次dispatch,action为ActionTypes.INIT,ActionTypes.INIT为Redux内部的action)。
每一个reducer都不能返回undefined。
第二个判断其实我并不是很能理解,不过从抛出错误的信息可以知道。
大意就是要求我们不要去处理Redux内部的action,对于未知的aciton都要返回一个不是undefined的数据。
Redux内部的action有三个。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 const randomString = ( Math .random ().toString (36 ).substring (7 ).split ("" ).join ("." ); const ActionTypes = { INIT : `@@redux/INIT${randomString()} ` , REPLACE : `@@redux/REPLACE${randomString()} ` , PROBE_UNKNOWN_ACTION : () => `@@redux/PROBE_UNKNOWN_ACTION${randomString()} ` , };
第三部分的代码到这里就结束,主要对reducer的返回值做了断言,并将断言的结果保存在shapeAssertionError中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 return function combination (state = {}, action ) { if (shapeAssertionError) { throw shapeAssertionError; } if (process.env .NODE_ENV !== "production" ) { const warningMessage = getUnexpectedStateShapeWarningMessage ( state, finalReducers, action, unexpectedKeyCache ); if (warningMessage) { warning (warningMessage); } } let hasChanged = false ; const nextState = {}; for (let i = 0 ; i < finalReducerKeys.length ; i++) { const key = finalReducerKeys[i]; const reducer = finalReducers[key]; const previousStateForKey = state[key]; const nextStateForKey = reducer (previousStateForKey, action); if (typeof nextStateForKey === "undefined" ) { const errorMessage = getUndefinedStateErrorMessage (key, action); throw new Error (errorMessage); } nextState[key] = nextStateForKey; hasChanged = hasChanged || nextStateForKey !== previousStateForKey; } hasChanged = hasChanged || finalReducerKeys.length !== Object .keys (state).length ; return hasChanged ? nextState : state; };
第四部分代码。
就是返回一个新的reducer函数了。
开始就先对之前保存的断言就行了判断,如果发现reducer不符合规则,直接抛出错误。
接下来。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 if (process.env .NODE_ENV !== "production" ) { const warningMessage = getUnexpectedStateShapeWarningMessage ( state, finalReducers, action, unexpectedKeyCache ); if (warningMessage) { warning (warningMessage); } }
这一段代码传入了旧的state,reducers数组,请求的action,和之前没用过的一个空的unexpectedKeyCache对象。
看看getUnexpectedStateShapeWarningMessage这个函数的实现。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 function getUnexpectedStateShapeWarningMessage ( inputState, reducers, action, unexpectedKeyCache const reducerKeys = Object .keys (reducers); const argumentName = action && action.type === ActionTypes .INIT ? "preloadedState argument passed to createStore" : "previous state received by the reducer" ; if (reducerKeys.length === 0 ) { return ( "Store does not have a valid reducer. Make sure the argument passed " + "to combineReducers is an object whose values are reducers." ); } if (!isPlainObject (inputState)) { return ( `The ${argumentName} has unexpected type of "` + {}.toString .call (inputState).match (/\s([a-z|A-Z]+)/ )[1 ] + `". Expected argument to be an object with the following ` + `keys: "${reducerKeys.join('", "' )} "` ); } const unexpectedKeys = Object .keys (inputState).filter ( (key ) => !reducers.hasOwnProperty (key) && !unexpectedKeyCache[key] ); unexpectedKeys.forEach ((key ) => { unexpectedKeyCache[key] = true ; }); if (action && action.type === ActionTypes .REPLACE ) return ; if (unexpectedKeys.length > 0 ) { return ( `Unexpected ${unexpectedKeys.length > 1 ? "keys" : "key" } ` + `"${unexpectedKeys.join('", "' )} " found in ${argumentName} . ` + `Expected to find one of the known reducer keys instead: ` + `"${reducerKeys.join('", "' )} ". Unexpected keys will be ignored.` ); } }
这个函数主要就是检查inputState的结构是否符合reducers。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 let hasChanged = false ;const nextState = {};for (let i = 0 ; i < finalReducerKeys.length ; i++) { const key = finalReducerKeys[i]; const reducer = finalReducers[key]; const previousStateForKey = state[key]; const nextStateForKey = reducer (previousStateForKey, action); if (typeof nextStateForKey === "undefined" ) { const errorMessage = getUndefinedStateErrorMessage (key, action); throw new Error (errorMessage); } nextState[key] = nextStateForKey; hasChanged = hasChanged || nextStateForKey !== previousStateForKey; }
这个循环便是整个返回函数中最重要的部分了。
定义了一个标志变量和hasChange和一个下一个状态的对象nextState。
循环已经筛选过的reducers,也就是finalReducerKeys。
key reducer的名字;reducer key对应的reducer;previousStateForKey reducer对应的旧状态;nextStateForKey reducer执行后的新状态。
然后判断新的状态是不是undefined,是的话报错,因为这是不符合规则的。
然后在新的状态对象上添加对应key为nextState。
最后确定新的状态是不是和旧的状态是否相同,保存在hasChange中。
1 2 3 hasChanged = hasChanged || finalReducerKeys.length !== Object .keys (state).length ; return hasChanged ? nextState : state;
最后就是确定要不要返回新的状态,如果每个reducer返回的都和旧状态相同的话。
逻辑上整个状态就应该和原来相同。
除了循环内的判断,最后做了一个finalReducerKeys.length !== Object.keys(state).length判断。
只要旧的state的key值集合长度和finalReducerKeys的长度不一致就返回nextState。
到这里基本上就把这个函数看完了。
需要注意的是,在文档中有对这函数的一个注意事项。
本函数设计的时候有点偏主观,就是为了避免新手犯一些常见错误。也因些我们故意设定一些规则,但如果你自己手动编写根redcuer时并不需要遵守这些规则。combineReducers 的 reducer 都需满足以下规则:
所有未匹配到的action,必须把它接收到的第一个参数也就是那个state原封不动返回。
永远不能返回undefined。当过早return时非常容易犯这个错误,为了避免错误扩散,遇到这种情况时combineReducers会抛异常。
如果传入的state就是undefined,一定要返回对应reducer的初始state。根据上一条规则,初始state禁止使用undefined。使用ES6的默认参数值语法来设置初始state很容易,但你也可以手动检查第一个参数是否为 undefined。
虽然combineReducers自动帮你检查reducer是否符合以上规则,但你也应该牢记,并尽量遵守。即使你通过 Redux.createStore(combineReducers(...), initialState) 指定初始state,combineReducers 也会尝试通过传递 undefined的state来检测你的reducer是否符合规则。因此,即使你在代码中不打算实际接收值为undefined的state,也必须保证你的reducer在接收到undefined时能够正常工作。
所以在源码中可以看到很多判断语句。